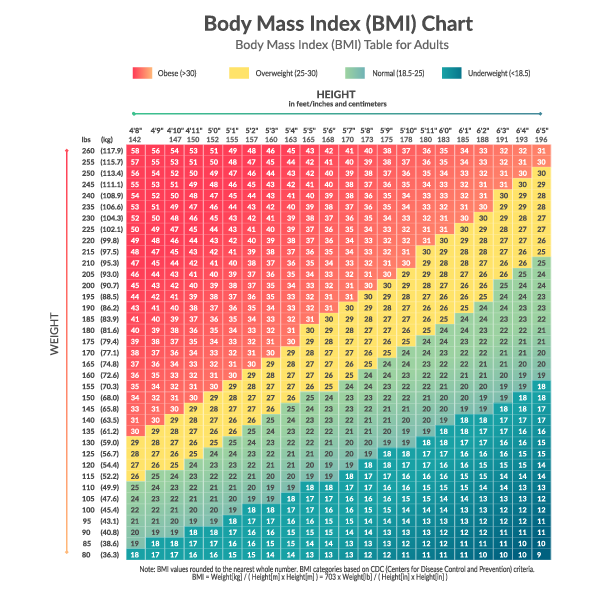
Have you ever wondered how workers in the health field assess health risk factors from a person-to-person basis? One way health workers like doctors, personal trainers, and health coaches deduct how healthy a person may or may not be is by assessing if they are in a healthy weight range or not. The most common standard for assessing this is by calculating someone’s BMI or Body Mass Index. When looking at BMI a person is capable of falling into four separate categories, Underweight, Healthy Weight, Overweight, and Obese. This article today is an attempt to teach you, the reader, about the different types of health risk factors that are associated with each category!
Disclaimer: There is one limiting factor when it comes to assessing BMI. That limiting factor would be that it does not account for “fat free mass”. Fat free mass would be things like bone, organs, water, but most importantly in this case muscle. Since muscle weighs more than fat some individuals, most commonly athletes, will proportionally carry a lot more muscle than they do fat which can make them weight more bumping them up into a higher weight category. BMI is the Ultimate standard for in assessing body weight for normal adults, not athletes who train nearly every day.
Categories:
Underweight:
Any BMI under 18.5 would be considered underweight.
Risk factors:
- Malnutrition
- Vitamin deficiencies
- Osteoporosis
- Infertility
- Developmental delays
- Decreased immune function
Healthy Weight:
Any BMI between 18.5 – 24.9 would be considered healthy weight.
Benefits:
- Lowers risk for developing health problems like:
- Heart disease, High blood pressure, Type 2 diabetes
- Labored breathing
- Colon cancer, kidney cancer, liver cancer, ovarian cancer.
- Increased energy levels
- Less joint pressure
Overweight & Obese:
Any BMI between 25 – 29.9 would be considered overweight while any BMI over 30 is considered obese.
Risk factors: The Health Effects of Overweight and Obesity | Healthy Weight, Nutrition, and Physical Activity | CDC
- Increased risk for mortality
- Increased risk of elevated cholesterol
- Increased risk for type 2 diabetes
- Increased risk for heart disease & stroke
- Increased risk for cancer
- Sleep apnea/breathing problems
- Low quality of life
Ways to achieve a healthy BMI:
- Exercise between 150 – 300 minutes per week.
- Focus on Eating whole foods instead of processed foods.
- Track daily activity and nutritional habits.
- Set various types of health goals.
- Stay consistent no matter how small the habit is!